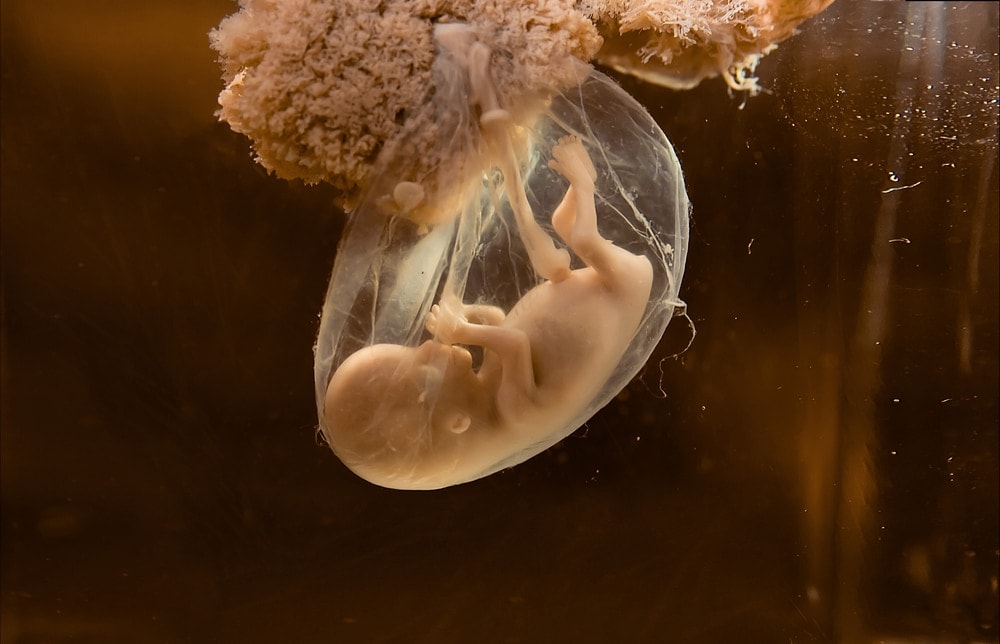
Tu bebé desarollará dentro de tu útero con la ayuda del sistema de soporte vital del feto compuesto de la placenta, cordón umbilical y saco amniótico (lo que se llena de líquido amniótico).
¿Qué es la placenta y qué hace?
La placenta ha estado descrito como un organo en forma de panqueque que se adhiere a la parte interior del útero y está conectado al feto por el cordón umbilical. La placenta produce hormonas relacionado con el embarazo, incluyendo gonadotropina coriónica humana (GCH), el estrógeno, la progesterona.
La placenta es responsable para trabajar como un puesto de operaciones entre el suministro de la sangre de la madre y el bebé. Los pequeños vasos sanguíneos que llevan la sangre del feto corren a través de la placenta, la cual está llena de sangre materna. Los nutrientes y el oxígeno de la sangre de la madre se transfieren a la sangre fetal, mientras que los productos de desecho se transfieren desde la sangre fetal a la sangre materna, sin la mezcla de los dos suministros de sangre.
La placenta está expulsado del útero en un proceso llamado el nacimiento póstumo. Un problema posible en el embarazo es placenta previa, donde la placenta se une cerca o sobre la cerviz. A medida que el feto crece, la presión sobre la placenta puede causar sangrado. Esta condición requiere tratamiento médico para garantizar un parto seguro para tu y tu bebé.
¿Qué es el cordón umbilical y qué hace?
El cordón umbilical es la linea de la vida que une la placenta al feto. El cordón umbilical está hecho de tres vasos sanguíneos: dos arterias más pequeñas que llevan la sangre a la placenta y una vena grande que devuelve la sangre al feto. Puede crecer estar 60 cm de largo, lo que permite bastante cordón para el bebé mover alrededor con seguridad sin causar daños en el cordón o la placenta.
Después del nacido del bebé, el cordón está cortado (algo que el padre del bebé puede desear hacer); a sección restante sanará y formará el ombligo del bebé. Durante el embarazo, puede averiguar que el cordón umbilical es en un nudo o que se envuelve alrededor de una parte del cuerpo de tu bebé. Esto común y no puede estar evitado y por lo general no representa ninguna amenaza para el bebé.
¿Cuál es el saco amniótico y qué hace?
El saco amniótico está lleno de líquido amniótico. Este saco es casa, gimnasio, y la protección de tu bebé contra golpes externos y otras presiones externas.
El saco amniótico permite un amplio espacio para el feto nadar y moverse para que ayuda a construir el tono muscular. Para mantener al bebé acogedor, el saco amniótico y su líquido mantienen una temperatura ligeramente más alta que el cuerpo de la madre, por lo general 99.7 F.
A semana 10, hay acerca de 30 ml de fluido presente. El fluido amniótico alcanzará su pico alrededor semanas 34-36 a casi 1 litro. Cuando se rompe la fuente, es el saco que ruptura y este fluido que sale del cuerpo. La vida de tu bebé está apoyado todavía por el cordón umbilical y ¡debes conocer tu bebé pronto!
¿Son la placenta, el cordón umbilical, y el saco amniótico diferente cuando se trata de nacimientos múltiples?
Los gemelos idénticos suelen compartir la misma placenta, por lo general tienen sacos amnióticos separados, y siempre tienen sus propios cordones umbilicales. Los mellizos tienen placentas separadas, sacos amnióticos separados, y sus propios cordones umbilicales.