During pregnancy, in order to protect your growing baby, it’s important to prioritize your health. This can be a challenge for women who have sexually transmitted diseases and become pregnant, or who contract one while pregnant. What about Gonorrhea in pregnancy?
It is not impossible to have a safe and healthy pregnancy while having Gonorrhea. You just want to work carefully with your doctor and take all the appropriate steps to ensure the health of your baby. Gonorrhea in pregnancy does not mean you will not have a healthy baby.
What is Gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is a highly contagious STD that infects both men and women and is spread through vaginal, anal and oral sex with a partner who has Gonorrhea. If untreated, the bacteria spreads from the site of infection within days or weeks. The good news is that gonorrhea can be cured with the right treatment.
What are the symptoms of gonorrhea in pregnancy?
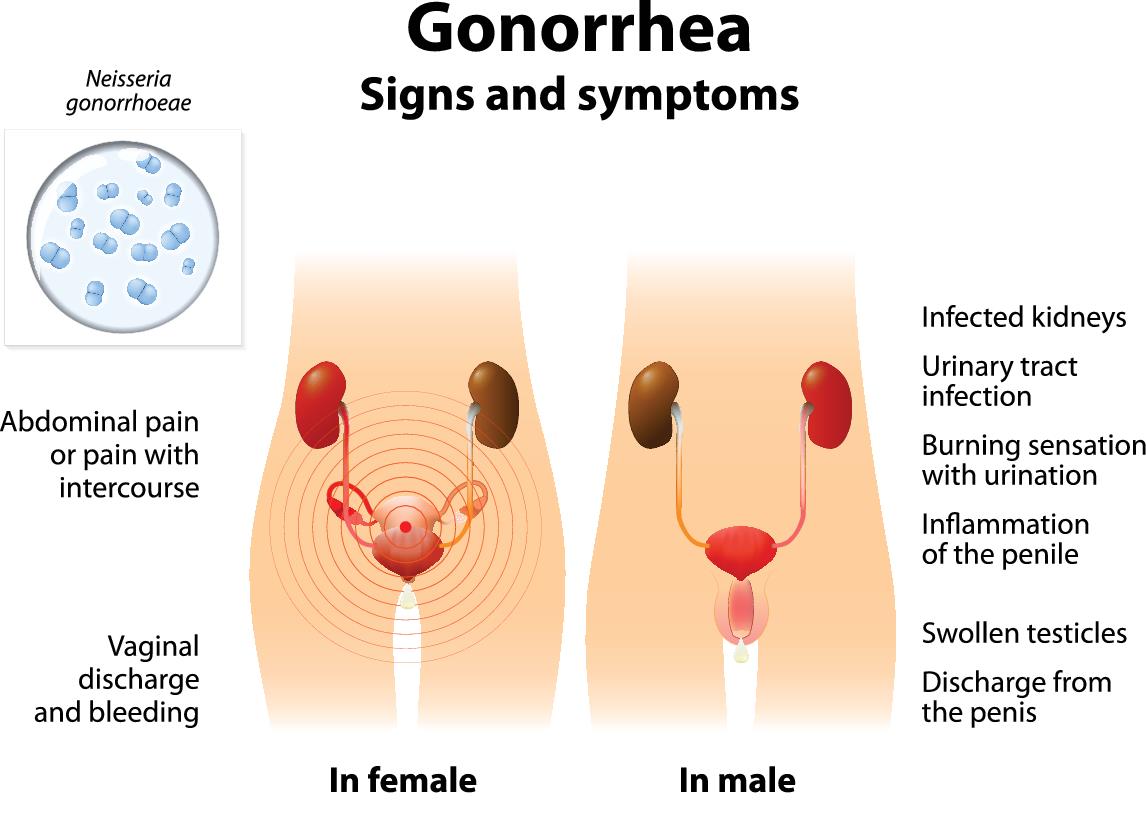
Gonorrhea can be notoriously hard to diagnose because it may not manifest itself with any obvious signs right away. For many people infected with gonorrhea the first sign is if a partner, past or current, begins developing symptoms.
Some men may not show any symptoms, but other men report symptoms that include:
- Burning while urinating
- Discharge from penis
- Swollen and tender testicles
Similar to men, women may not experience any symptoms right away. Early symptoms may even be mistaken for a bladder infection. However, this does not mean that serious complications won’t arise from gonorrhea despite the lack of symptoms.
Symptoms of gonorrhea in women may include:
- Painful urination
- Increase in vaginal discharge
- Irregular vaginal bleeding
- Anal itching
- Soreness of the anus (for both men and women)
- Bleeding from the anus (for both men and women)
- Painful bowel movements (for both men and women)
Generally, if treated, gonorrhea can be completely eliminated. However, long term effects may occur with delayed treatment.
Long term risks and effects may include:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which causes scar tissue that can block fallopian tubes, ectopic pregnancies, infertility, and chronic pelvic pain.
How do you treat gonorrhea during pregnancy?
In order to prevent complications during pregnancy, it is recommended that you get screened for gonorrhea while pregnant at your first prenatal visit so you receive proper treatment. This will decrease the chances of complications as a result of gonorrhea as well as the risk of passing it on to your baby.
Gonorrhea, if untreated, can lead to an increased risk in miscarriage and premature birth. In addition, gonorrhea can be passed from mother to newborn baby during vaginal delivery, which can lead to a severe eye infection if left untreated.
If detected, gonorrhea is very easily treated in the infant. The traditional treatment for uncomplicated gonorrhea s a dose of ceftriaxone, which is also safe for pregnant mothers and infants.
Can Gonorrhea be prevented?
There are only two 100% effective ways to prevent Gonorrhea. The first is to refrain from sexual contact of any kind. The second is to be in a long-term monogamous relationship such as marriage.
The use of condoms does reduce the risk of transmission of Gonorrhea, but it does not prevent it. According to a study presented at the 2002 National STD Prevention Conference, there is a 50% risk reduction by using condoms.
Want to Know More?
- For more information on Gonorrhea download the Gonorrhea – CDC Fact Sheet here.
- Vaginal Discharge During Pregnancy
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Pregnancy
Sources Used
Harms, R. W. (2004). Mayo Clinic guide to a healthy pregnancy. New York: HarperResource.
Kliegman, R. (2007). Nelson textbook of pediatrics (18th ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders.
M.D., R. J. (1994). Lifestyle During Pregnancy. Mayo Clinic Complete Book of Pregnancy and Baby’s First Year. New York: William Morrow and Company Inc.